
Harnessing the Power of FEA
Part 1: Introducing Finite Element Analysis
By Amin Moghaddas
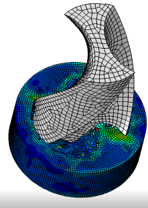
parameters using FEA
Finite Element Analysis (FEA) is a powerful numerical method used to solve complex engineering problems, particularly those involving intricate geometries, loadings, and material properties where analytical solutions may not be feasible. By breaking down complex systems into smaller elements, FEA allows engineers to accurately predict how structures will respond to various forces and conditions. FEA helps shorten product development time, reduces testing and redesign costs, identifies potential issues before manufacturing, and optimizes performance prior to prototyping.
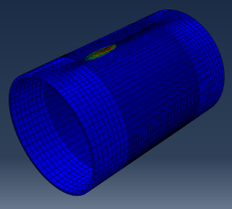
stress in a gas metal arc-welded pipe
At EWI, we harness the capabilities of FEA — a key element of our integrated computational materials engineering (ICME) strategy — to provide our clients with insights that drive innovation, enhance safety, and improve performance across various industries. Join us over the next few weeks as we explore EWI capabilities in performing different types of FEA to address industry challenges such as evaluation of formability of new materials, reduction of material waste in metal forming, reduction of residual stress and distortion in different welding processes, tool design optimization in power ultrasonic applications, and development of failure criteria for crash analysis!
The FEA that will be covered includes:
- Structural analysis
- Vibration analysis
- Thermal analysis
- Mass diffusion analysis
- Analysis of non-linear dynamic processes
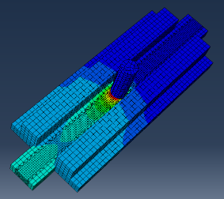
welded extrusions
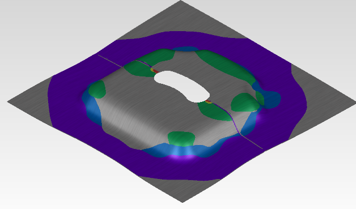
laser-welded sheet metals
Amin Moghaddas is an Applications Engineer in the EWI resistance and solid-state group with more than 15 years of expertise in Finite Element Analysis (FEA). His primary focus is computational modeling of thermal processes, specializing in predicting temperature profile, residual stress, and distortion. Amin also has deep expertise in vibration analysis, designing and fabricating tooling for ultrasonic systems. Additionally, he is highly skilled in the structural analysis of components, including both static and dynamic simulations.