
Harnessing the Power of Finite Element Analysis
Part 3: Vibrational Analysis
By Amin Moghaddas
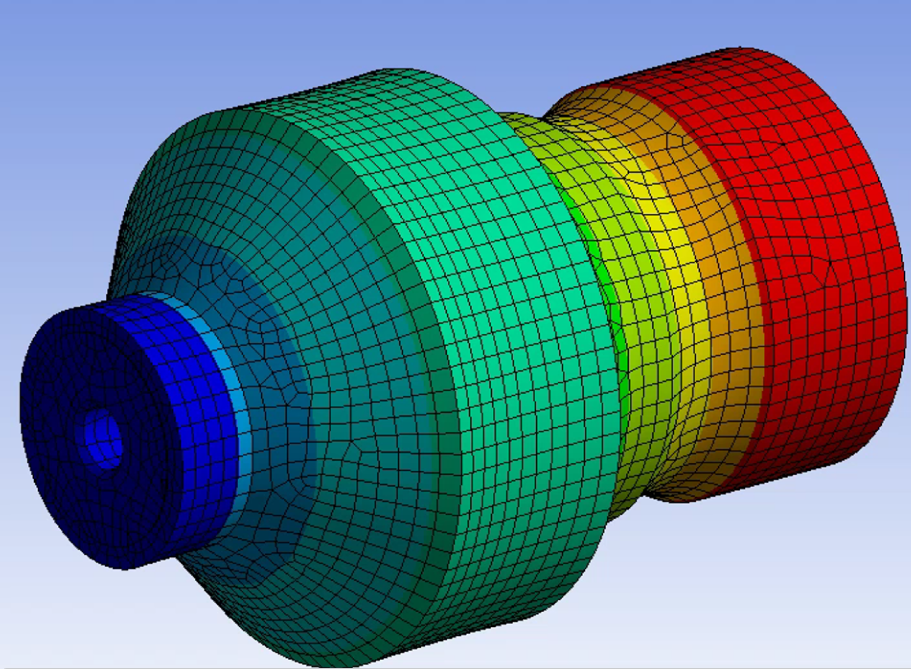
plastic welding application
Vibrational analysis helps us understand how structures and components respond to dynamic loads. When it comes to power ultrasonic applications like ultrasonic metal or plastic welding processes, precise tooling design is critical for success.
One of the key components of tooling in these systems is the ultrasonic horn, which needs to be designed to run at specific frequency, with certain amplitude and acceptable stress level to ensure smooth performance and efficient energy transfer. This is where Finite Element Analysis (FEA) plays a significant role.
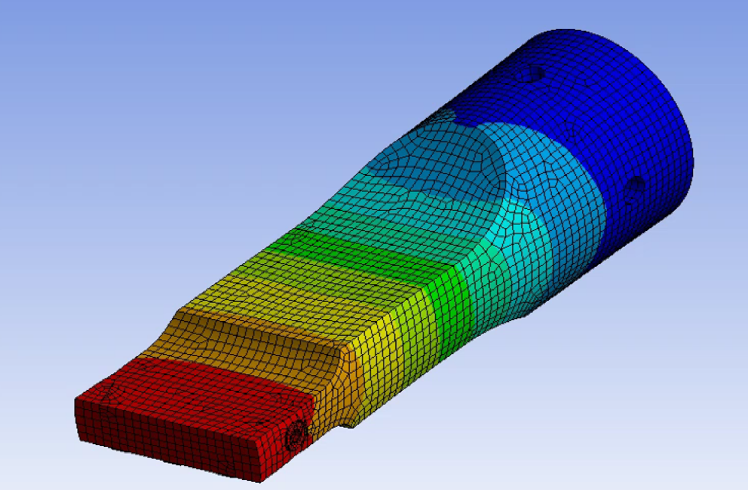
on a bi-metal horn
By leveraging FEA in vibration analysis, we can simulate the dynamic behavior of ultrasonic horns, predict their resonance frequencies, and optimize their geometries to make sure uniform amplitude can be generated on the face of the horn. This helps to reduce redesign and manufacturing costs and time by eliminating the trial-and-error approach, identify premature failure (that could lead to cracks) and parasitic modes in designs before manufacturing any tools and optimize performance by tailoring horn design for different welding applications.

To find out how vibration analysis can be used for your application to reduce the manufacturing time and costs, please contact [email protected] to discuss how we can use our FEA tools to assist you!
Read other articles in this series:
- Part 1: Introducing Finite Element Analysis
- Part 2: Harnessing the Power of FEA: Structural Analysis
Amin Moghaddas is an Applications Engineer in the EWI resistance and solid-state group with more than 15 years of expertise in Finite Element Analysis (FEA). His primary focus is computational modeling of thermal processes, specializing in predicting temperature profile, residual stress, and distortion. Amin also has deep expertise in vibration analysis, designing and fabricating tooling for ultrasonic systems. Additionally, he is highly skilled in the structural analysis of components, including both static and dynamic simulations.